

Great for biologists and environmentalists, these flash cards cover the factors going into ecology
There are 67 flash cards in this set (12 pages to print.)
To use:
1. Print out the cards.
2. Cut along the dashed lines.
3. Fold along the solid lines.
Sample flash cards in this set:



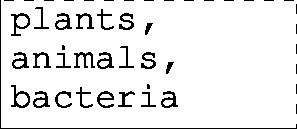
| Questions | Answers |
|---|---|
| Ecology | the scientific study of the interactions between different kinds of living things and their environment |
| biotic factors | plants, animals, bacteria |
| ecologist | a scientist who studies ecology |
| abiotic factors | climate, light, soil, water |
| biosphere | includes all organisms and the environments in which they live (biotic and abiotic factors) |
| organism | an individual living thing |
| population | includes all the organisms in the same species in a given area. |
| community | a collection of populations that interact with each other in a given area |
| ecosystem | includes all biotic and abiotic factors in a given area |
| biome | a group of ecosystems in the same region having similar types of vegetation governed by similar climatic conditions. |
| population density | the number of organisms living in a given area. |
| growth rate | the change in population size |
| exponential growth | when ideal conditions allow organisms to reproduce at a rate greater then their death rate |
| logistic growth | Available resources become more limited as a population increases, causing the population to slow and stabilize |
| carrying capacity | the point at which the population becomes stable |
| density-dependent limiting factors | competition, predation, parasitism, crowding/stress |
| Density-Independent Limiting Factors | Weather, Fire, Drought/Flood, Human Activities |
| niche | the role that a species plays in its community |
| habitat | the place where the organism lives |
| succession | the natural change that takes place within a community of an ecosystem |
| Primary Succession | the gradual development of a new community where no organisms have lived before. |
| Primary Succession | no soil present |
| Primary Succession | mosses and lichens are the pioneer species |
| Climax Community | A stable community |
| Secondary Succession | Occurs when a natural disaster or human activity partially destroys a community. |
| Secondary Succession | Soil is already present. |
| Secondary Succession | Species replacing the pioneer species are different. |
| Secondary Succession | Takes less time to become a climax community. |
| Renewable Resource | A natural resource that is replaced or replenished by natural processes. |
| Renewable Resource | Soil, plants, water, crops, animals, gas, oil |
| Nonrenewable Resource | Those that are available in limited amounts |
| Nonrenewable Resource | Metals, Minerals, Topsoil, Fossil fuels |
| Pollution | the contamination of soil, water, or air as a result of human activity |
| Air Pollution | caused primarily by the burning of fossil fuels to produce electricity, or driving cars, and heating homes. |
| Smog | A combination of smoke, gases, and fog. Contains Sulfur oxides. |
| Acid Rain | Smog reacts with water vapor in the atmosphere to produce sulfuric acid |
| Greenhouse Effect | Burning of fossil fuels release excess carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. The excess gas traps radiant energy from the sun. The atmosphere prevents the heat from escaping. |
| Ozone Layer | The layer which protects of from lethal doses of ultraviolet radiation |
| Greenhouse Effect | Allows the Earth to remain warm enough for living things to survive. |
| Ozone Layer | This layer is thinning because of CFC's (chlorofluorocarbons) |
| Water Pollution | Caused by contaminants from sewers, industries, farms, and homes entering water sources. |
| Causes of Water Pollution | Sewage, Fertilizer, dirty wash water |
| Greenhouse Effect | Causes glacial melting which could result in flooding of coastal regions |
| Three Rs | Reduce, Reuse, Recycle |
| Tropism | a plant's response to its environment |
| Geotropism | a plant's response to gravity |
| Phototropism | a plant's response to light |
| Thigmotropism | a plant's response to touch |
| Hormones | a chemical messenger used by plants to control their growth in response to environmental stimuli |
| Auxin | Hormone responsible for regulation phototropism, by stimulating the elongation of cells. |
| Auxin | Ex: Causes stems to bend; promotes fruit growth and dropping of fruit; causes leaf loss in the fall |
| Gibberellins | Growth hormone that causes plants to grow taller |
| Abscisic Acid | inhibits plant growth & cell division during times of stress |
| Behavior | anything an animal does in response to stimuli in its environment |
| Innate Behavior | inherited behavior of animals |
| Reflex | automatic response that requires no thinking at all |
| Instinct | complex pattern of innate behaviors |
| Instinct | behaviors which may take longer and may be a combination of behaviors |
| Instinct | courtship |
| Reflex | happens within seconds |
| Territory | a physical space that contains the breeding ground, feeding areas, shelter, or potential mates of an animal |
| Migration | the instinctive, seasonal movement of a species |
| Hibernate | a condition in which the animal's body temperature drops, oxygen consumption decreases, and breathing rates decrease to just a few breaths per minute. |
| Estivation | a condition in which animals reduce the rate of their metabolisms due to extreme heat, lack of food, or long periods of drought |
| Learned Behavior | a result of previous experiences of an animal that modifies their current behavior |
| Habituation | when an animal is repeatedly given a stimulus that is not harmful and does not have a negative impact on the animal |
| Imprinting | a form of learned behavior; A process whereby a young animal follow the characteristics of his/her mother after hatching |