
Learn about the policies and changes involved in different economies.
There are 42 flash cards in this set (7 pages to print.)
To use:
1. Print out the cards.
2. Cut along the dashed lines.
3. Fold along the solid lines.
Sample flash cards in this set:




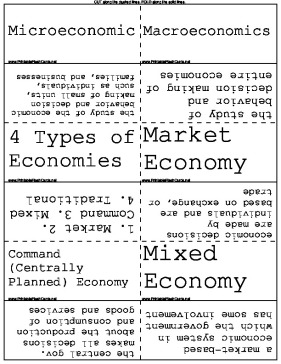
| Questions | Answers |
|---|---|
| Microeconomic | the study of the economic behavior and decision making of small units, such as individuals, families, and businesses |
| Macroeconomics | the study of behavior and decision making of entire economies |
| 4 Types of Economies | 1. Market 2. Command 3. Mixed 4. Traditional |
| Market Economy | economic decisions are made by individuals and are based on exchange, or trade |
| Command (Centrally Planned) Economy | the central gov. makes all decisions about the production and consumption of goods and services |
| Mixed Economy | a market-based economic system in which the government has some involvement |
| Traditional Economy | rely on habit, custom, or ritual to decide what to produce, how to produce it, and to whom to distribute it |
| 3 Factors of Production | land, labor, and capital; the three groups of resources that are used to make all goods and services |
| Land | natural resources used to make goods and resources |
| Labor | the effort that people devote to a task for which they are paid |
| Capital | any human-made resource that is used to create other goods and services |
| What are the 3 questions that every country must answer? | 1. What goods and services should be produced? 2. How should these goods and services be produced? 3. Who consumes these goods and serivces? |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | the total value of all final goods and services produced in a particular economy |
| Trade offs | all the alternatives that we sacrifice when we make a decision |
| Opportunity Costs | the most desirable alternative given up as the result of a decision |
| Elasticity of Demand | a measure of how consumers respond to price changes |
| Elastic | describes demand that is very sensitive to a change in price |
| Inelastic | describes demand that is not very sensitive to price changes |
| Scarcity | limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants |
| General Partnership | partners share equally in both responsibility and liability |
| Law of Demand | consumers will buy more of a good when its price is lower and less when its price is higher |
| Law of Supply | tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price |
| Budget Surplus | A situation in which budget revenues exceed expenditures |
| Limited Partnership | one partner is required to be a general partner or to have unlimited personal liability for the firm |
| Vertical Merger | the combination of two or more firms involved in different stages of producing the same good or service |
| Horizontal Merger | the combination of two or more firms competing in the same market with the same good or service |
| Corporation | a legal entity, or being, owned by individual stockholders, each of whom has limited liability for the firm's debts |
| Price Ceiling | a maximum price that can legally be charged for a good or service |
| Price Floor | a minimum price for a good or service |
| Different Types of Partnerships | 1. General Partnership 2. Limited Partnership 3. Limited Liability Partnership |
| Franchise | a contract that gives a single firm the right to sell goods within an exclusive market |
| Monopoly | a market in which a single seller dominates |
| Variable Expenses | kinds of spending that can be controlled and typically change from month to month |
| Fixed Expenses | Expenses which stay basically the same from month to month, such as housing and transportation |
| Inflation | a general increase in prices across an economy |
| Bank | an institution for receiving, keeping, and lending money |
| Limited Liability Partnership | newer type of partnership; all partners are limited partners |
| Sole Proprietorship Advantages | 1. Ease of Start-Up 2. Relatively Few Regulations 3. Sole Receiver of Profit 4. Full Control 5. Easy to Discontinue |
| Monopolistic Competition | a market structure in which many companies sell products that are similar but nor identical |
| Budget Deficits | a situation in which budget expenditures exceed revenues |
| What is deficit spending? | government spending, in excess of revenue, of funds raised by borrowing rather than from taxation |
| Sole Proprietorship | a business owned and managed by a single individual |